This article introduces to you how we can use dependency injection is your application to perform curd operations. To implement Dependency Inject pattern, we will use Ninject Dependency Injector.To know more about dependency injection, you could visit my tip here: Constructor Dependency Injection Pattern Implementation in C#.
Our Roadmap Towards Learning MVC with Entity Framework
- Relationship in Entity Framework Using Code First Approach With Fluent API.
- Code First Migrations with Entity Framework
- CRUD Operations Using Entity Framework 5.0 Code First Approach in MVC
- CRUD Operations Using the Repository Pattern in MVC
- CRUD Operations Using the Generic Repository Pattern and Unit of Work in MVC
- CRUD Operations Using the Generic Repository Pattern and Dependency Injection in MVC
Dependency Injection (DI)
Dependency Injection (DI) is a type of IoC, it is a pattern where objects are not responsible for creating their own dependencies. Dependency injection is a way to remove hard-coded dependencies among objects, making it easier to replace an object's dependencies, either for testing (using mock objects in unit test) or to change run-time behaviour.
Before understanding Dependency Injection, you should be familiar with the two concepts of Object Oriented Programming, one is tight coupling and another is loose coupling, so let's see each one by one.
Tight Coupling
When a class is dependent on a concrete dependency, it is said to be tightly coupled to that class. A tightly coupled object is dependent on another object; that means changing one object in a tightly coupled application often requires changes to a number of other objects. It is not difficult when an application is small but in an enterprise level application, it is too difficult to make the changes.
Loose Coupling
It means two objects are independent and an object can use another object without being dependent on it. It is a design goal that seeks to reduce the inter-dependencies among components of a system with the goal of reducing the risk that changes in one component will require changes in any other component.
Now in short, Dependency Injection is a pattern that makes objects loosely coupled instead of tightly coupled. Generally, we create a concrete class object in the class we require the object and bind it in the dependent class but DI is a pattern where we create a concrete class object outside this high-level module or dependent class.
There are three types of dependency injections:
- Constructor Dependency Injection
- Setter Dependency Injection
- Interface Dependency Injection
In this article, we will use Constructor Dependency Injection. This is the most commonly used Dependency Injection Pattern in Object Oriented Programming. The Constructor Dependency Injection uses a parameter to inject dependencies so there is normally one parameterized constructor always. So in this constructor dependency, the object has no default constructor and you need to pass specified values at the time of creation to initiate the object. You can say that your design is loosely coupled with the use of constructor dependency injection.
Dependency Injection (DI) Container
The Dependency Injection Container is a framework to create dependencies and inject them automatically when required. It automatically creates objects based on requests and injects them when required. It helps us split our application into a collection of loosely-coupled, highly-cohesive pieces and then glue them back together in a flexible manner. By DI container, our code will become easier to write, reuse, test and modify. In this article, we will use a Niject DI Container.
CRUD Operations Application Design
We create four projects in a solution to implement DIP with generic repository pattern. These are:
Ioc.Core(class library)Ioc.Data(class library)Ioc.Service(class library)Ioc.Web(web application)
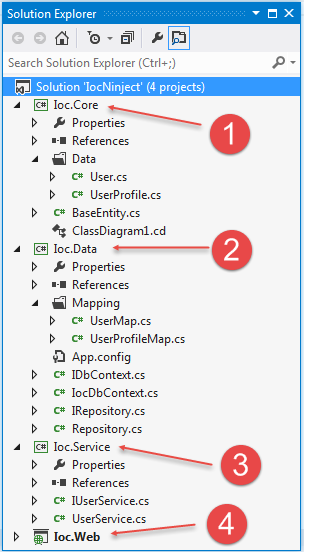
Figure 1.1: Application Project Structure
Define Entities in Application
In this article, we are working with the Entity Framework Code First Approach so the project
Ioc.Core contains entities that are necessary in the application's database. In this project, we create three entities, one is theBaseEntity class that has common properties that will be inherited by each entity and the others are Userand UserProfile entities. Let's see each entity. The following is a code snippet for the BaseEntity class.using System;
namespace Ioc.Core
{
public abstract class BaseEntity
{
public Int64 ID { get; set; }
public DateTime AddedDate { get; set; }
public DateTime ModifiedDate { get; set; }
public string IP { get; set; }
}
}
The
User and UserProfile entities have a one-to-one relationship. One User can have only one profile.
Figure 1.2: Relationship between User and UserProfile Entities
Now, we create a User entity under the Data folder of the
Ioc.Core project that inherits from the BaseEntityclass. The following is a code snippet for the User entity.using System;
namespace Ioc.Core.Data
{
public class User : BaseEntity
{
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public virtual UserProfile UserProfile { get; set; }
}
}
Now, we create a
UserProfile entity under the Data folder of the Ioc.Core project that inherits from theBaseEntity class. The following is a code snippet for the UserProfile entity.using System;
namespace Ioc.Core.Data
{
public class UserProfile : BaseEntity
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public virtual User User { get; set; }
}
}
Define Context Class
The
Ioc.Data project contains DataContext, User and UserProfile entities Mapping and Repository. The ADO.NET Entity Framework Code First data access approach requires us to create a data access context class that inherits from the DbContext class so we create an interface IDbContext that inherited by context classIocDbContext (IocDbContext.cs) class. In this class, we override the OnModelCreating() method. This method is called when the model for a context class (IocDbContext) has been initialized, but before the model has been locked down and used to initialize the context such that the model can be further configured before it is locked down. First, create an IDbContext interface and the following code snippet for it.using System.Data.Entity;
using Ioc.Core;
namespace Ioc.Data
{
public interface IDbContext
{
IDbSet<TEntity> Set<TEntity>() where TEntity : BaseEntity;
int SaveChanges();
}
}
Now, create the
IocDbContext class and the following code snippet for it.using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Ioc.Core;
namespace Ioc.Data
{
public class IocDbContext : DbContext, IDbContext
{
public IocDbContext()
: base("name=DbConnectionString")
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
var typesToRegister = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetTypes()
.Where(type => !String.IsNullOrEmpty(type.Namespace))
.Where(type => type.BaseType != null && type.BaseType.IsGenericType &&
type.BaseType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(EntityTypeConfiguration<>));
foreach (var type in typesToRegister)
{
dynamic configurationInstance = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
modelBuilder.Configurations.Add(configurationInstance);
}
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
public new IDbSet<TEntity> Set<TEntity>() where TEntity : BaseEntity
{
return base.Set<TEntity>();
}
}
}
As you know, the EF Code First approach follows convention over configuration, so in the constructor, we just pass the connection string name, the same as an App.Config file and it connects to that server. In the
OnModelCreating() method, we used reflection to map an entity to its configuration class in this specific project.Define Mapping of Entities
Now, we define the configuration for the
User and UserProfile entities that will be used when the database table will be created by the entity. The configuration defines the class library project Ioc.Data under theMapping folder. Now create the configuration classes for the entity. For the User entity, we create the UserMapclass and for the UserProfile entity, create the UserProfileMap class.
The following is a code snippet for the
UserMap class.using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
namespace Ioc.Data.Mapping
{
public class UserMap :EntityTypeConfiguration<User>
{
public UserMap()
{
//key
HasKey(t => t.ID);
//properties
Property(t => t.UserName).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.Email).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.Password).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.AddedDate).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.ModifiedDate).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.IP);
//table
ToTable("Users");
}
}
}
The following is a code snippet for the
UserProfileMap class.using System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
namespace Ioc.Data.Mapping
{
public class UserProfileMap : EntityTypeConfiguration<UserProfile>
{
public UserProfileMap()
{
//key
HasKey(t => t.ID);
//properties
Property(t => t.FirstName).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(100).HasColumnType("nvarchar");
Property(t => t.LastName).HasMaxLength(100).HasColumnType("nvarchar");
Property(t => t.Address).HasColumnType("nvarchar");
Property(t => t.AddedDate).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.ModifiedDate).IsRequired();
Property(t => t.IP);
//table
ToTable("UserProfiles");
//relation
HasRequired(t => t.User).WithRequiredDependent(u => u.UserProfile);
}
}
}
Create Generic Repository
The Repository pattern is intended to create an abstraction layer between the data access layer and the business logic layer of an application. It is a data access pattern that prompts a more loosely coupled approach to data access. We create the data access logic in a separate class, or set of classes, called a repository, with the responsibility of persisting the application's business model.
Now, we create a generic repository interface and class. This generic repository has all CRUD operations methods. This repository contains a parameterized constructor with a parameter as Context so when we create an instance of the repository, we pass a context so that all the repositories for each entity has the same context. We are using the
saveChanges() method of the context. The following is a code snippet for the Generic Repository interface.using System.Linq;
using Ioc.Core;
namespace Ioc.Data
{
public interface IRepository<T> where T : BaseEntity
{
T GetById(object id);
void Insert(T entity);
void Update(T entity);
void Delete(T entity);
IQueryable<T> Table { get; }
}
}
The following is a code snippet for the Generic Repository class that implements the interface.
IRepository using System;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Data.Entity.Validation;
using System.Linq;
using Ioc.Core;
namespace Ioc.Data
{
public class Repository<T> : IRepository<T> where T: BaseEntity
{
private readonly IDbContext _context;
private IDbSet<T> _entities;
public Repository(IDbContext context)
{
this._context = context;
}
public T GetById(object id)
{
return this.Entities.Find(id);
}
public void Insert(T entity)
{
try
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
this.Entities.Add(entity);
this._context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx)
{
var msg = string.Empty;
foreach (var validationErrors in dbEx.EntityValidationErrors)
{
foreach (var validationError in validationErrors.ValidationErrors)
{
msg += string.Format("Property: {0} Error: {1}",
validationError.PropertyName, validationError.ErrorMessage) + Environment.NewLine;
}
}
var fail = new Exception(msg, dbEx);
throw fail;
}
}
public void Update(T entity)
{
try
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
this._context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx)
{
var msg = string.Empty;
foreach (var validationErrors in dbEx.EntityValidationErrors)
{
foreach (var validationError in validationErrors.ValidationErrors)
{
msg += Environment.NewLine + string.Format("Property: {0} Error: {1}",
validationError.PropertyName, validationError.ErrorMessage);
}
}
var fail = new Exception(msg, dbEx);
throw fail;
}
}
public void Delete(T entity)
{
try
{
if (entity == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("entity");
}
this.Entities.Remove(entity);
this._context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException dbEx)
{
var msg = string.Empty;
foreach (var validationErrors in dbEx.EntityValidationErrors)
{
foreach (var validationError in validationErrors.ValidationErrors)
{
msg += Environment.NewLine + string.Format("Property: {0} Error: {1}",
validationError.PropertyName, validationError.ErrorMessage);
}
}
var fail = new Exception(msg, dbEx);
throw fail;
}
}
public virtual IQueryable<T> Table
{
get
{
return this.Entities;
}
}
private IDbSet<T> Entities
{
get
{
if (_entities == null)
{
_entities = _context.Set<T>();
}
return _entities;
}
}
}
}
Create Service for User Operations
To implement DIP with DI, we create a service for the user entity that the service communicates with the UI and data access logic. Since DIP states that a high-level module should not depend on a low-level module we define an
IUsesService interface in the Ioc.Service project depending on what we need on the UI to do the CRUD operations. The following code snippet is for IUserService.using System.Linq;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
namespace Ioc.Service
{
public interface IUserService
{
IQueryable<User> GetUsers();
User GetUser(long id);
void InsertUser(User user);
void UpdateUser(User user);
void DeleteUser(User user);
}
}
Now, we create a concrete
UserService class that implemented the IUserService interface to do CRUD operations on both User and UserProfile entities using generic repository. The following code snippet is for the UserService class in the same project.using System.Linq;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
using Ioc.Data;
namespace Ioc.Service
{
public class UserService : IUserService
{
private IRepository<User> userRepository;
private IRepository<UserProfile> userProfileRepository;
public UserService(IRepository<User> userRepository, IRepository<UserProfile> userProfileRepository)
{
this.userRepository = userRepository;
this.userProfileRepository = userProfileRepository;
}
public IQueryable<User> GetUsers()
{
return userRepository.Table;
}
public User GetUser(long id)
{
return userRepository.GetById(id);
}
public void InsertUser(User user)
{
userRepository.Insert(user);
}
public void UpdateUser(User user)
{
userRepository.Update(user);
}
public void DeleteUser(User user)
{
userProfileRepository.Delete(user.UserProfile);
userRepository.Delete(user);
}
}
}
An MVC Application Using the IoC and DI
In this section, we use a fourth project,
Ioc.Web, to design the user interface so that we can do CRUD operations on both User and UserProfile entities.Ninject Dependency Injection Container
The Ninject is a lightweight dependency injection framework for .NET applications. It helps us split our application into a collection of loosely-coupled, highly-cohesive pieces and then glue them back together in a flexible manner. By using Ninject to support our application's architecture, our code will become easier to write, reuse, test and modify. You can learn more about it from http://www.ninject.org/.

Figure 1.3: Our Hero Ninject Dependency Injector
First of all, we need to install Ninject.MVC4 Nuget package in our web application, in other words in the
Ioc.Webproject.
Figure 1.4: Ninject.MVC4 Nuget Package
This package also installed the dependent page and our application has the following packages after its installation.
NinjectNinject.MVC4Ninject.Web.CommonNinject.Web.Common.WebHost
After its installation, the
NinjectWebCommon class is created under the App_Start folder of the web application. The following code snippet is for this class:[assembly: WebActivatorEx.PreApplicationStartMethod
(typeof(Ioc.Web.App_Start.NinjectWebCommon), "Start")]
[assembly: WebActivatorEx.ApplicationShutdownMethodAttribute
(typeof(Ioc.Web.App_Start.NinjectWebCommon), "Stop")]
namespace Ioc.Web.App_Start
{
using System;
using System.Web;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
using Ioc.Data;
using Ioc.Service;
using Microsoft.Web.Infrastructure.DynamicModuleHelper;
using Ninject;
using Ninject.Web.Common;
public static class NinjectWebCommon
{
private static readonly Bootstrapper bootstrapper = new Bootstrapper();
/// <summary>
/// Starts the application
/// </summary>
public static void Start()
{
DynamicModuleUtility.RegisterModule(typeof(OnePerRequestHttpModule));
DynamicModuleUtility.RegisterModule(typeof(NinjectHttpModule));
bootstrapper.Initialize(CreateKernel);
}
/// <summary>
/// Stops the application.
/// </summary>
public static void Stop()
{
bootstrapper.ShutDown();
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates the kernel that will manage your application.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The created kernel.</returns>
private static IKernel CreateKernel()
{
var kernel = new StandardKernel();
try
{
kernel.Bind<Func<IKernel>>().ToMethod(ctx => () => new Bootstrapper().Kernel);
kernel.Bind<IHttpModule>().To<HttpApplicationInitializationHttpModule>();
RegisterServices(kernel);
return kernel;
}
catch
{
kernel.Dispose();
throw;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Load your modules or register your services here!
/// </summary>
/// <param name="kernel">The kernel.</param>
private static void RegisterServices(IKernel kernel)
{
kernel.Bind<IDbContext>().To<IocDbContext>().InRequestScope();
kernel.Bind(typeof(IRepository<>)).To(typeof(Repository<>)).InRequestScope();
kernel.Bind<IUserService>().To<UserService>();
}
}
}
In the
RegisterServices() method of the preceding code, we bind the interface to the concrete classes. By this, the concrete class object assigned to bind the interface instance.CRUD Operations Model and Controller
Our user interface form is common for both
User and UserProfile entities so we create a model depending on the model. We define UserModel (UserModel.cs) under the Models folder and the following code snippet for it.using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace Ioc.Web.Models
{
public class UserModel
{
public Int64 ID { get; set; }
[Display(Name ="First Name")]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[Display(Name="Last Name")]
public string LastName { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
[Display(Name="User Name")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
[Display(Name ="Added Date")]
public DateTime AddedDate { get; set; }
}
}
We create a controller to do these CRUD operations. Create a
UserController under the Controllers folder of the application. This controller has all the ActionResult methods for each user interface of a CRUD operation. We first create an IUserInterface instance, then the controller's constructor initiates the service using dependency injection. The following is a code snippet for the UserController.using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Ioc.Service;
using Ioc.Web.Models;
using Ioc.Core.Data;
namespace Ioc.Web.Controllers
{
public class UserController : Controller
{
private IUserService userService;
public UserController(IUserService userService)
{
this.userService = userService;
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult Index()
{
IEnumerable<UserModel> users = userService.GetUsers().Select(u => new UserModel
{
FirstName = u.UserProfile.FirstName,
LastName = u.UserProfile.LastName,
Email = u.Email,
Address = u.UserProfile.Address,
ID = u.ID
});
return View(users);
}
[HttpGet]
public ActionResult CreateEditUser(int? id)
{
UserModel model = new UserModel();
if (id.HasValue && id != 0)
{
User userEntity = userService.GetUser(id.Value);
model.FirstName = userEntity.UserProfile.FirstName;
model.LastName = userEntity.UserProfile.LastName;
model.Address = userEntity.UserProfile.Address;
model.Email = userEntity.Email;
model.UserName = userEntity.UserName;
model.Password = userEntity.Password;
}
return View(model);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult CreateEditUser(UserModel model)
{
if (model.ID == 0)
{
User userEntity = new User
{
UserName = model.UserName,
Email = model.Email,
Password = model.Password,
AddedDate = DateTime.UtcNow,
ModifiedDate = DateTime.UtcNow,
IP = Request.UserHostAddress,
UserProfile = new UserProfile
{
FirstName = model.FirstName,
LastName = model.LastName,
Address = model.Address,
AddedDate = DateTime.UtcNow,
ModifiedDate = DateTime.UtcNow,
IP = Request.UserHostAddress
}
};
userService.InsertUser(userEntity);
if (userEntity.ID > 0)
{
return RedirectToAction("index");
}
}
else
{
User userEntity = userService.GetUser(model.ID);
userEntity.UserName = model.UserName;
userEntity.Email = model.Email;
userEntity.Password = model.Password;
userEntity.ModifiedDate = DateTime.UtcNow;
userEntity.IP = Request.UserHostAddress;
userEntity.UserProfile.FirstName = model.FirstName;
userEntity.UserProfile.LastName = model.LastName;
userEntity.UserProfile.Address = model.Address;
userEntity.UserProfile.ModifiedDate = DateTime.UtcNow;
userEntity.UserProfile.IP = Request.UserHostAddress;
userService.UpdateUser(userEntity);
if (userEntity.ID > 0)
{
return RedirectToAction("index");
}
}
return View(model);
}
public ActionResult DetailUser(int? id)
{
UserModel model = new UserModel();
if (id.HasValue && id != 0)
{
User userEntity = userService.GetUser(id.Value);
// model.ID = userEntity.ID;
model.FirstName = userEntity.UserProfile.FirstName;
model.LastName = userEntity.UserProfile.LastName;
model.Address = userEntity.UserProfile.Address;
model.Email = userEntity.Email;
model.AddedDate = userEntity.AddedDate;
model.UserName = userEntity.UserName;
}
return View(model);
}
public ActionResult DeleteUser(int id)
{
UserModel model = new UserModel();
if (id != 0)
{
User userEntity = userService.GetUser(id);
model.FirstName = userEntity.UserProfile.FirstName;
model.LastName = userEntity.UserProfile.LastName;
model.Address = userEntity.UserProfile.Address;
model.Email = userEntity.Email;
model.AddedDate = userEntity.AddedDate;
model.UserName = userEntity.UserName;
}
return View(model);
}
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult DeleteUser(int id, FormCollection collection)
{
try
{
if ( id != 0)
{
User userEntity = userService.GetUser(id);
userService.DeleteUser(userEntity);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View();
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
}
}
Before starting the UI design, we have a look at its constructor, we are using
IUserService as the parameter of the constructor and here we are injecting the class object that binds from the IUserService interface in the Dependency Injection container.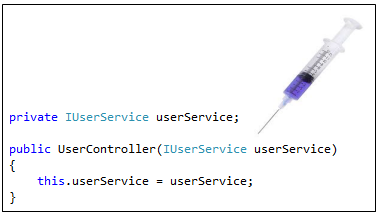
Figure 1.5: Dependency Inject
We have now developed the
UserController to handle the CRUD operations request for both the User andUserProfile entities. Thereafter we develop the user interface for the CRUD operations. We develop it for the views for adding and editing a user, a user listing, user delete and user details. Let's see each one by one.Create / Edit User View
We create a common view for creating and editing a user such as CreateEditUser.cshtml under the User folder of the views. Now define a create/edit user view and following is a code snippet for CreateEditUser.cshtml.
@model Ioc.Web.Models.UserModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create Edit User";
}
<div class="book-example panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading panel-head">Add / Edit User</div>
<div class="panel-body">
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
<div class="form-horizontal">
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.Email, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Password, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.PasswordFor(model => model.Password,new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.TextBoxFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-lg-9"></div>
<div class="col-lg-3">
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index", null, new { @class = "btn btn-default" })
<button class="btn btn-success" id="Button1" type="submit">
Submit
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
Now run the application and call the
CreateEditUser() action method with a HttpGet request, then we get the UI as in Figure 1.6 to add a new user to the application.
Figure 1.6: Add new user UI
User List View
This is the first view when the application is accessed or the entry point of the application is executed. It shows the user listing as in Figure 1.7. We display user data in tabular format and on this view, we create links to add a new user, edit a user, delete a user and the details of a user. This view is an index view and the following is a code snippet for index.cshtml under the User folder of the View.
@model IEnumerable<Ioc.Web.Models.UserModel>
<div class="book-example panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading panel-head">Users Listing</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<a id="A1" href="@Url.Action("CreateEditUser")"
class="btn btn-success">
<span class="glyphicon glyphicon-plus"></span> User
</a>
<table class="table" style="margin: 4px">
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayName("Name")
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Email)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Address)
</th>
<th>Action
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
@foreach (var item in Model)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.FirstName)
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem=>item.LastName)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Email)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Address)
</td>
<td>
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "CreateEditUser",
new { id = item.ID }, new { @class = "btn btn-success" })
@Html.ActionLink("Details", "DetailUser",
new { id = item.ID }, new { @class = "btn btn-primary" })
@Html.ActionLink("Delete", "DeleteUser",
new { id = item.ID }, new { @class = "btn btn-danger" })
</td>
</tr>
}
</table>
</div>
</div>
When we run the application and call the
index() action with an HttpGet request, then we get all the users listed in the UI as in Figure 1.11. This UI has options for CRUD operations.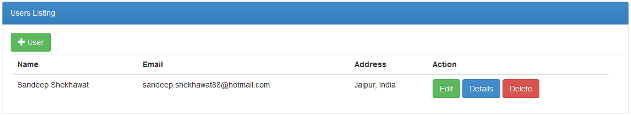
Figure 1.7: User Listing UI
As in the figure above, the user queue has an option for Edit. When we click on the Edit button, then the
CreateEditUser() action method is called with an HttpGet request and the UI is shown as in Figure 1.8.
Figure 1.8: Edit a User UI
Now, we change the input field data and click on the submit button, then the
CreateEditUser() action method is called with a HttpPost request and that user data is successfully updated in the database.User Detail View
We create a view that shows the specific user details when the details button is clicked in the user listing data. We call the
DetailUser() action method with a HttpGet request that shows a “Details” view such as in Figure 1.9 so we create a view DetailUser and the following is the code snippet for DetailUser.cshtml. @model Ioc.Web.Models.UserModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "User Detail";
}
<div class="book-example panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading panel-head">User Detail</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<div class="form-horizontal">
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Email, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.AddedDate, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.AddedDate, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-lg-2"></div>
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.ActionLink("Edit", "CreateEditUser",
new { id = ViewContext.RouteData.Values["id"] },
new { @class = "btn btn-primary" })
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index",
null, new { @class = "btn btn-success" })
</div>
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
</div>
Figure 1.9: User Detail UI
Delete User
Delete a user is the last operation of this article. To delete a user, we follow the process of clicking on the Delete button that exists in the User listing data. The user detail view then prompts to ask “You are sure you want to delete this?” after clicking on the Delete button that exists in the Delete view such as in Figure 1.10. When we click the Delete button of the user list, then it makes an
HttpGet request that calls the DeleteUser() action method that shows a delete view, then clicks on the Delete button of the view, then an HttpPost request makes that call to the ConfirmDeleteUser() action methods that delete that user. The following is a code snippet forDeleteUser.cshtml.@model Ioc.Web.Models.UserModel
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Delete User";
}
<div class="book-example panel panel-primary">
<div class="panel-heading panel-head">Delete User</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<h1>@ViewBag.ErrorMessage</h1>
<div class="form-horizontal">
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.FirstName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.LastName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.UserName, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Email, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
@Html.LabelFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "col-lg-2 control-label" })
<div class="col-lg-9">
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.Address, new { @class = "form-control" })
</div>
</div>
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
<div class="form-group">
<div class="col-lg-2"></div>
<div class="col-lg-9">
<input type="submit" value="Delete" class="btn btn-danger" />
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index", null, new { @class = "btn btn-success" })
</div>
</div>
}
</div>
</div>
</div>
Figure 1.10: Delete a User UI

Great Article
ReplyDeleteC# mvc training | Online MVC Training | asp.net mvc training in chennai